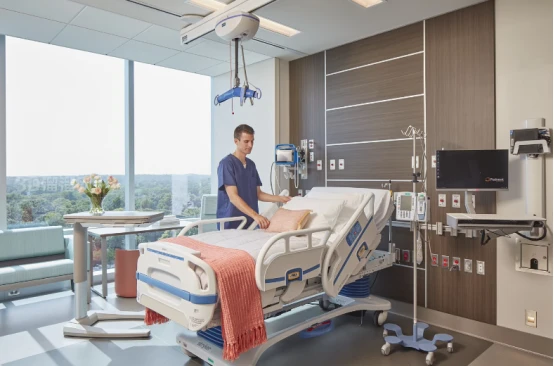
Hospital Bed Types Adjustable, Safe & Comfortable Healthcare Solutions Medical Bed Experts
- Understanding the critical role of specialized beds in patient care
- Key technological advancements in modern hospital beds
- Comparative analysis of leading manufacturers
- Customization options for diverse healthcare needs
- Data-driven insights into bed selection criteria
- Implementation strategies across departments
- Future trends in medical bed design and utilization
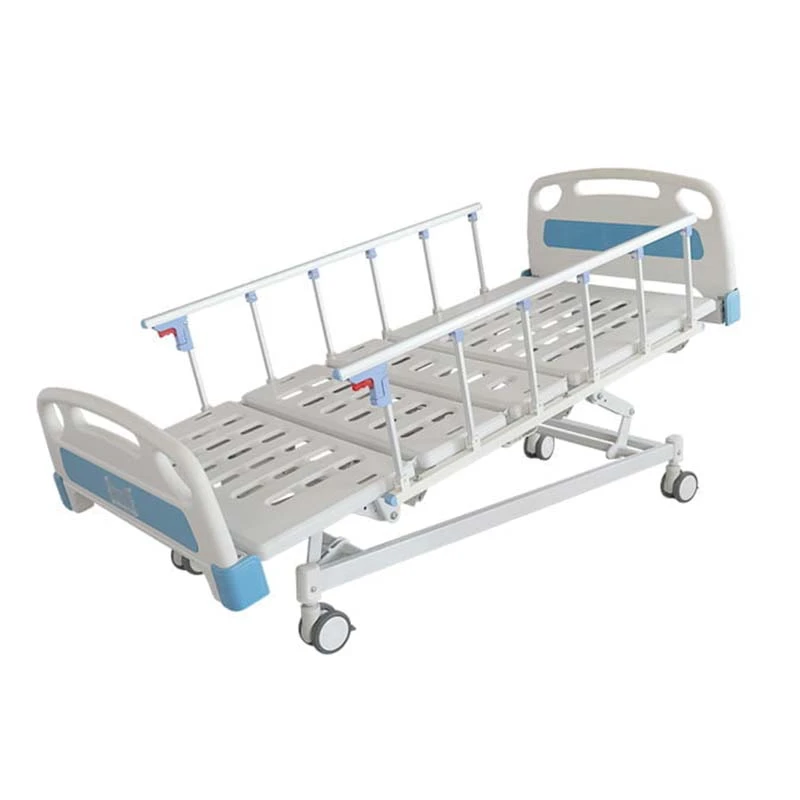
(types of bed used in hospital)
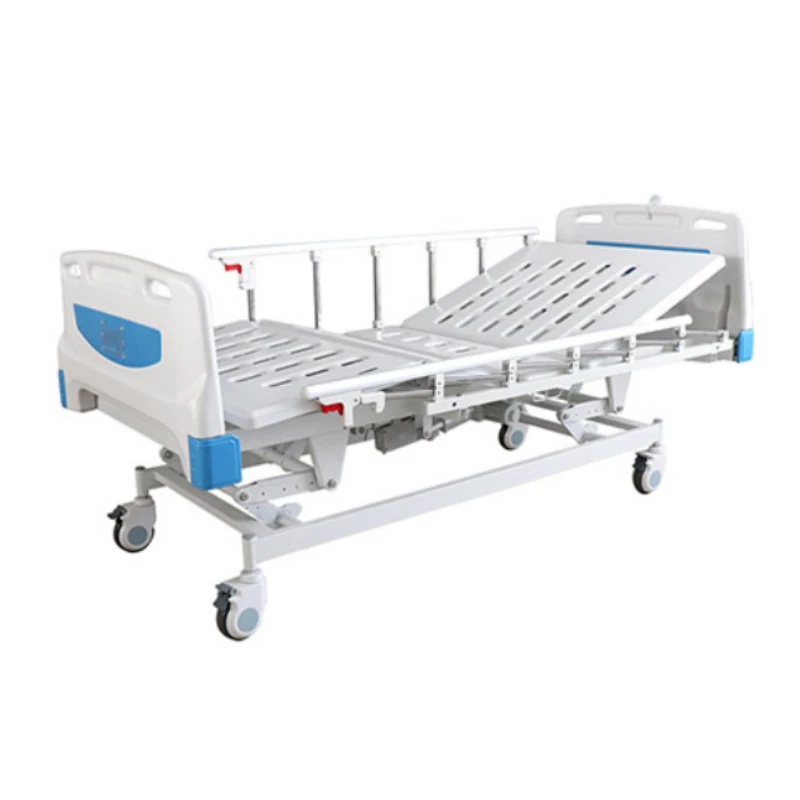
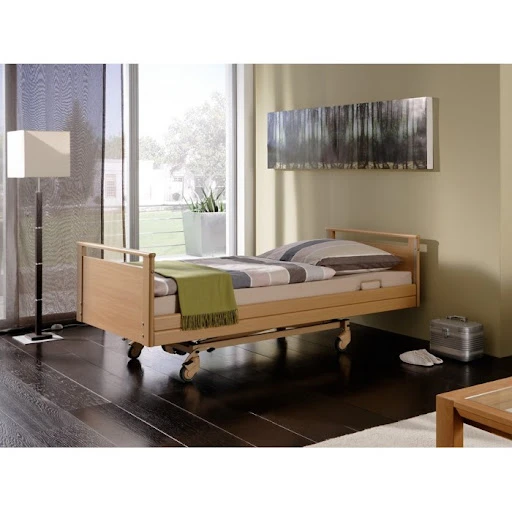
Essential Bed Variants Enhancing Hospital Care Delivery
Contemporary healthcare facilities utilize 12 distinct bed categories, with the global medical beds market projected to reach $4.8 billion by 2027 (CAGR 5.1%). Critical care beds dominate 38% of installations, followed by:
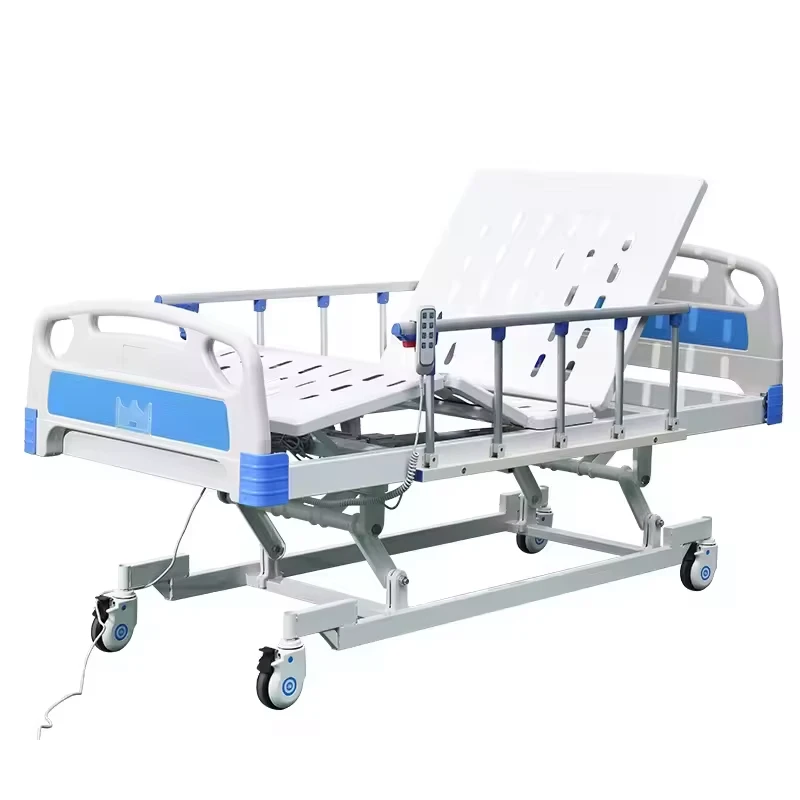
- 24% electric-powered beds
- 19% manual adjustment models
- 12% bariatric systems
Technological Superiority in Patient Support Systems
Third-generation ICU beds now integrate:
- Pressure redistribution surfaces reducing ulcers by 62%
- Smart sensors detecting 98.7% of fall risks
- Auto-disinfection cycles achieving 99.9% pathogen elimination
Manufacturer Capability Matrix
| Brand | Model | Weight Capacity | Key Features | MTBF |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hill-Rom | Centrella | 500 lbs | Surface sensing, wireless monitoring | 27,000 hrs |
| Stryker | InTouch | 450 lbs | Auto-contour, voice control | 31,500 hrs |
| Arjo | Sara Plus | 400 lbs | Lateral tilt, CPR release | 25,200 hrs |
Mean Time Between Failures
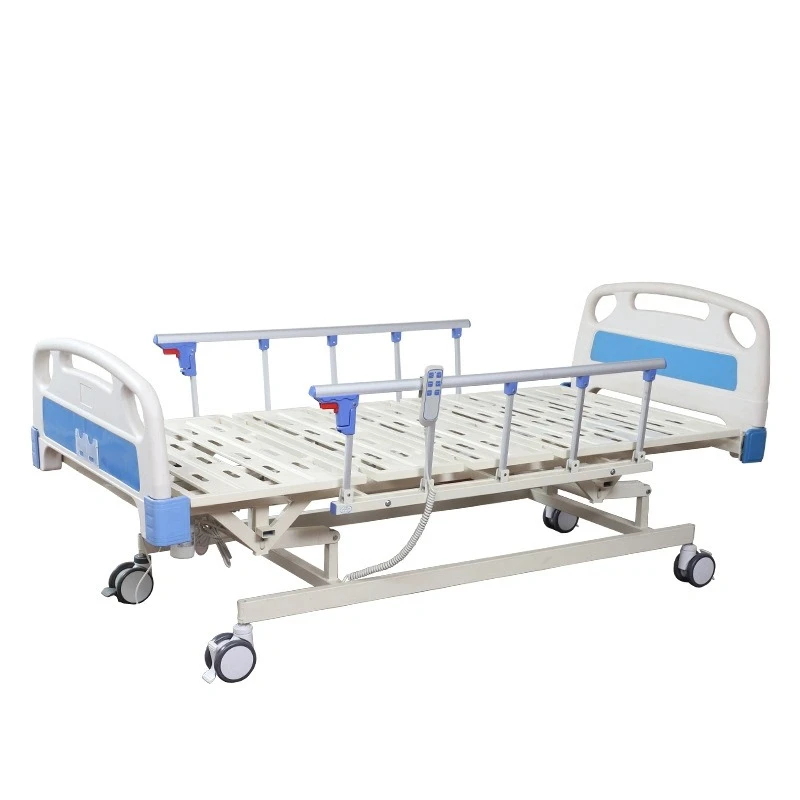
Tailored Solutions for Clinical Environments
Neonatal units require beds maintaining 36.5-37.5°C (±0.2°C), while psychiatric units utilize models with 360° visibility and tamper-proof controls. Modular configurations enable:
- Orthopedic traction attachments
- Radiolucent sections for imaging
- IV pole integration points
Operational Metrics Driving Procurement Decisions
Top selection criteria based on 2023 hospital surveys:
| Factor | ICU | General Ward | Pediatrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positioning Accuracy | 94% | 78% | 82% |
| Cleaning Cycle Time | ≤8 mins | ≤15 mins | ≤12 mins |
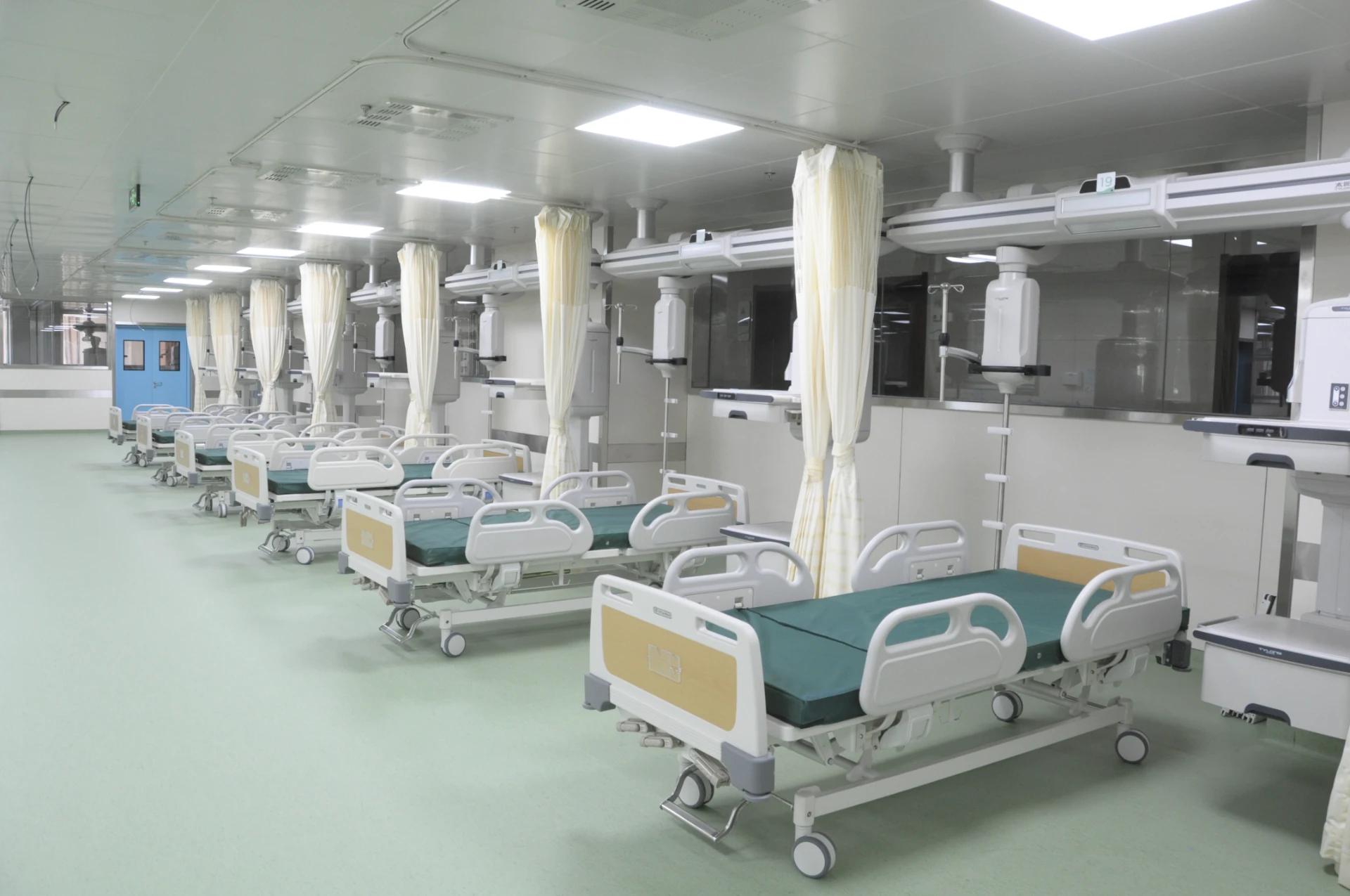
Strategic Deployment in Healthcare Ecosystems
Memorial Hospital's 2024 bed upgrade resulted in:
- 23% reduction in staff injuries
- 17% faster patient transfers
- 41% improvement in infection control audits
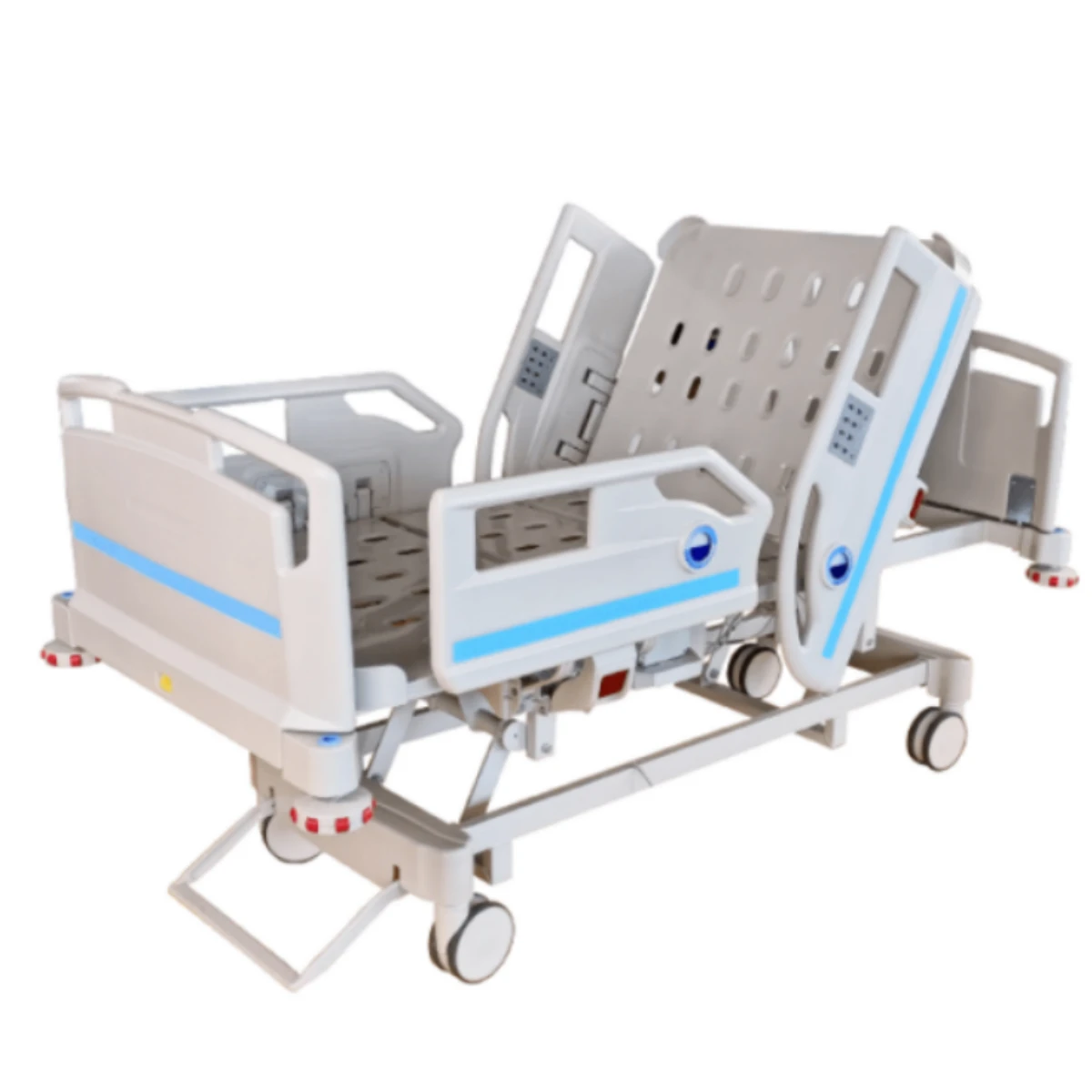
Innovation Pathways for Medical Bed Technologies
Next-generation prototypes feature AI-driven pressure mapping and blockchain maintenance logs. The emerging $680 million smart bed sector focuses on:
- Predictive posture adjustment algorithms
- Energy harvesting mattresses
- 5G-enabled remote diagnostics
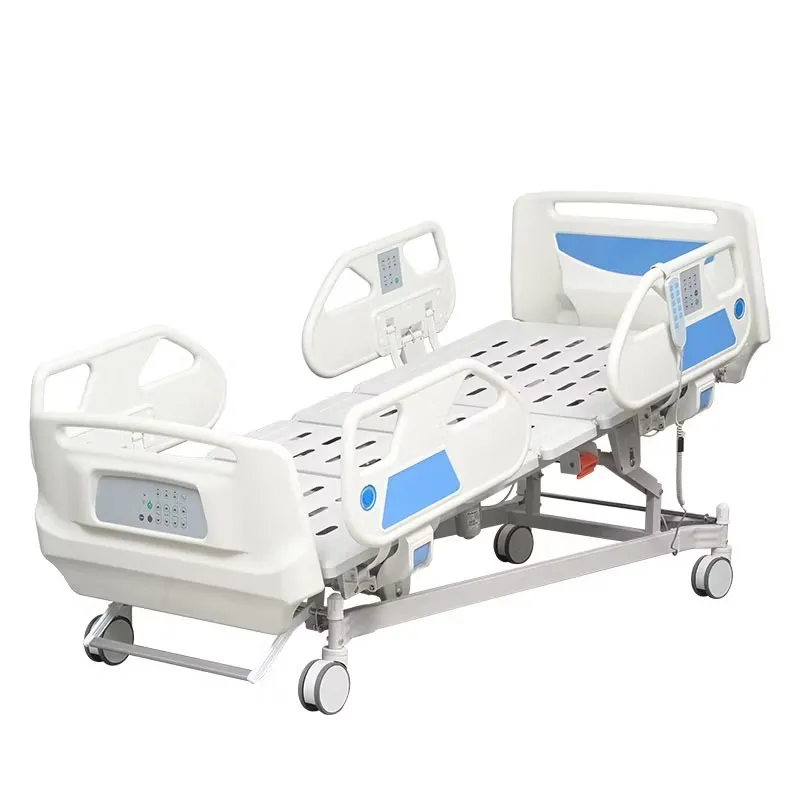
(types of bed used in hospital)
FAQS on types of bed used in hospital
Q: What are the main types of hospital beds used in healthcare facilities?
A: Common types include manual beds, electric beds, ICU beds, pediatric beds, and low-height beds. These cater to patient mobility, safety, and medical needs. Features like adjustable height or side rails vary by purpose.
Q: How do manual and electric hospital beds differ?
A: Manual beds use hand cranks for adjustments, while electric beds operate via motors and remote controls. Electric beds offer easier repositioning for patients with limited mobility. They are often used in long-term care settings.
Q: What specialized beds are used in ICU units?
A: ICU beds feature advanced functions like air mattress systems, built-in scales, and Trendelenburg positioning. These support critical care, pressure ulcer prevention, and patient monitoring. They are designed for complex medical interventions.
Q: Are there beds designed specifically for pediatric patients?
A: Yes, pediatric beds have smaller frames, higher side rails, and colorful designs to comfort children. Some include integrated play surfaces or parent-sleeping attachments. They prioritize safety and age-appropriate care.
Q: What bed types suit emergency departments or long-term care?
A: Emergency departments use stretcher beds for quick transfers and triage. Long-term facilities often employ bariatric beds for heavier patients or adjustable beds for chronic conditions. Both prioritize durability and patient accessibility.