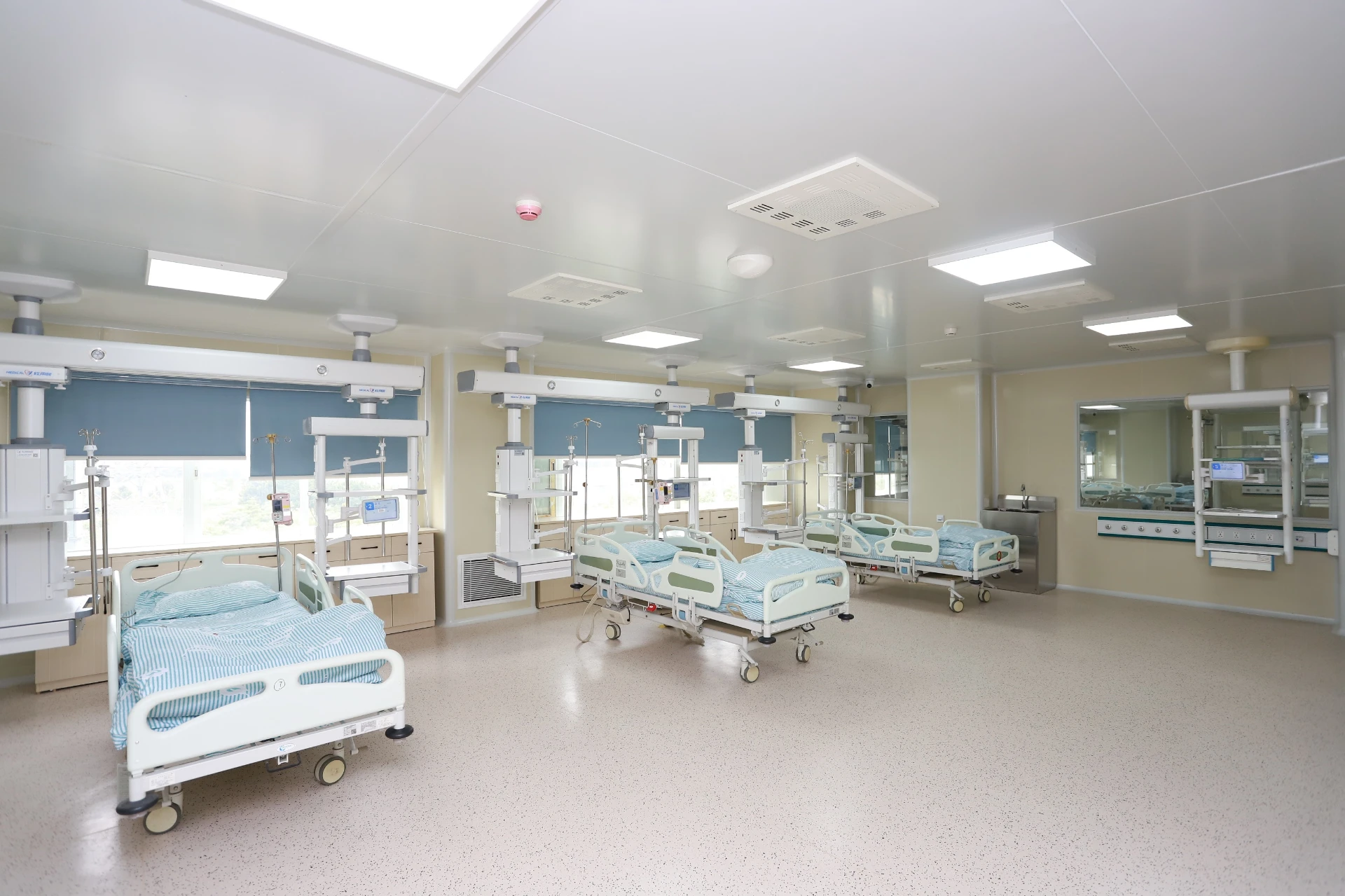
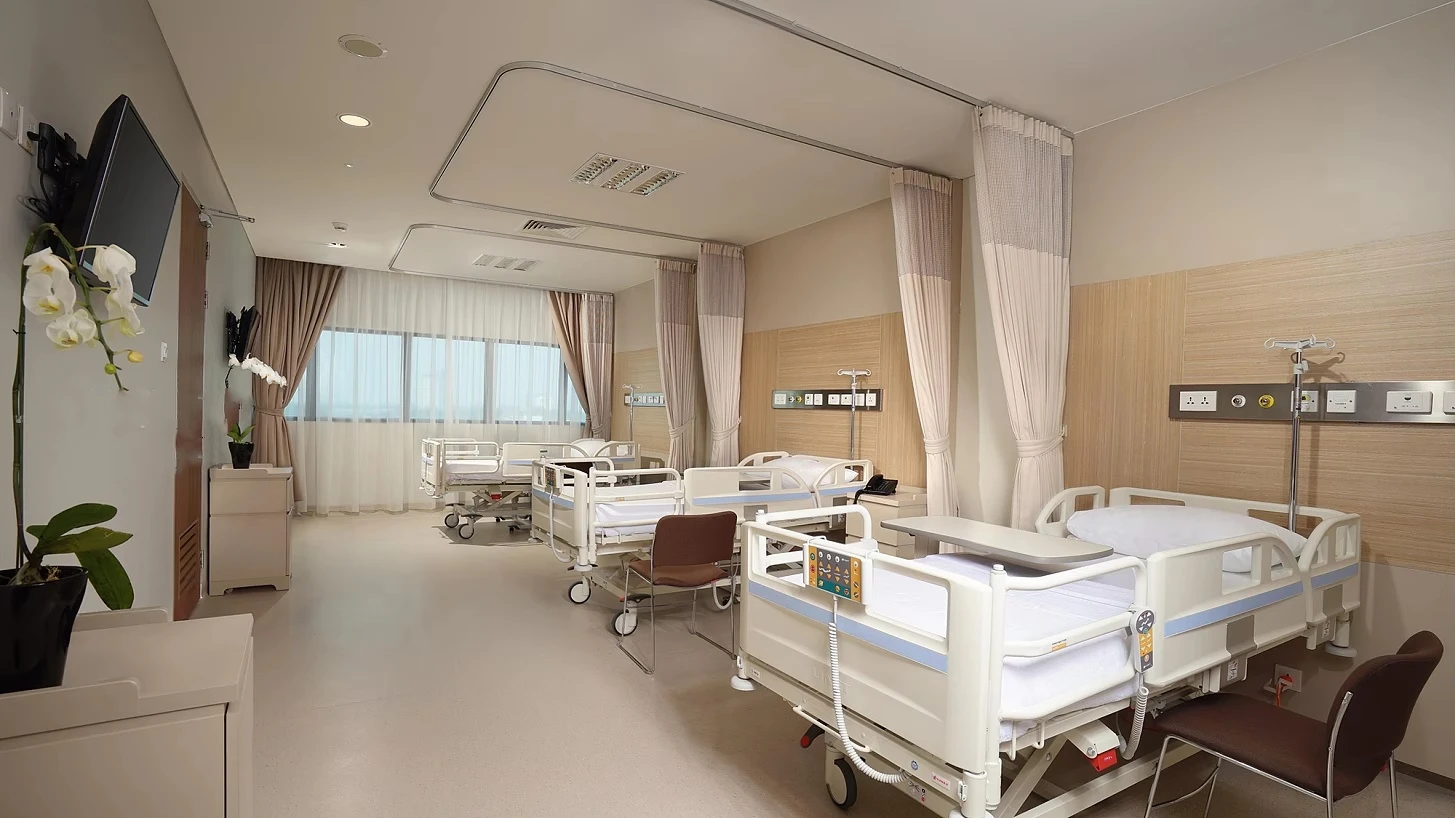
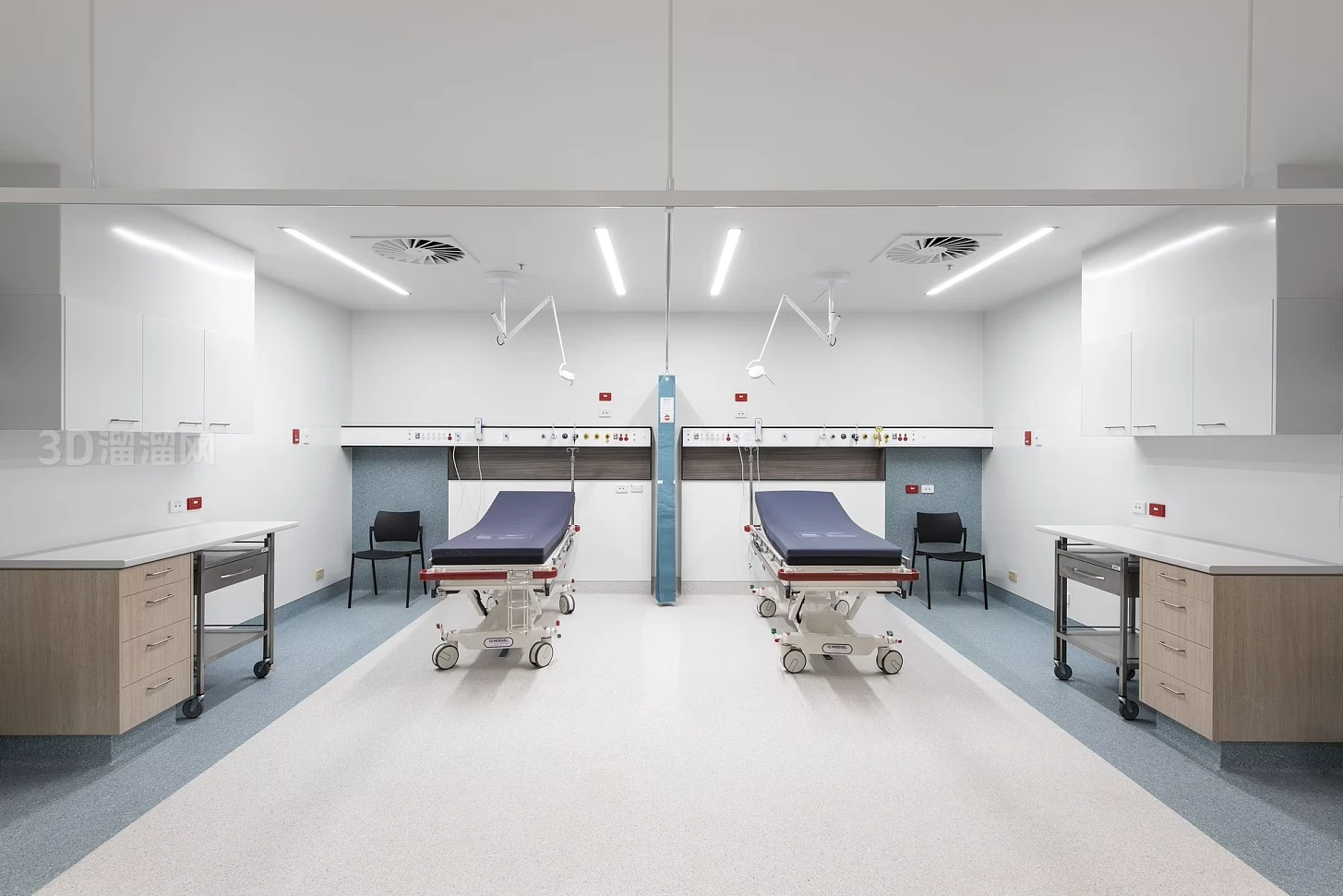
Types of ICU Beds and Their Importance in Critical Care
Types of ICU Beds and Their Features
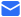
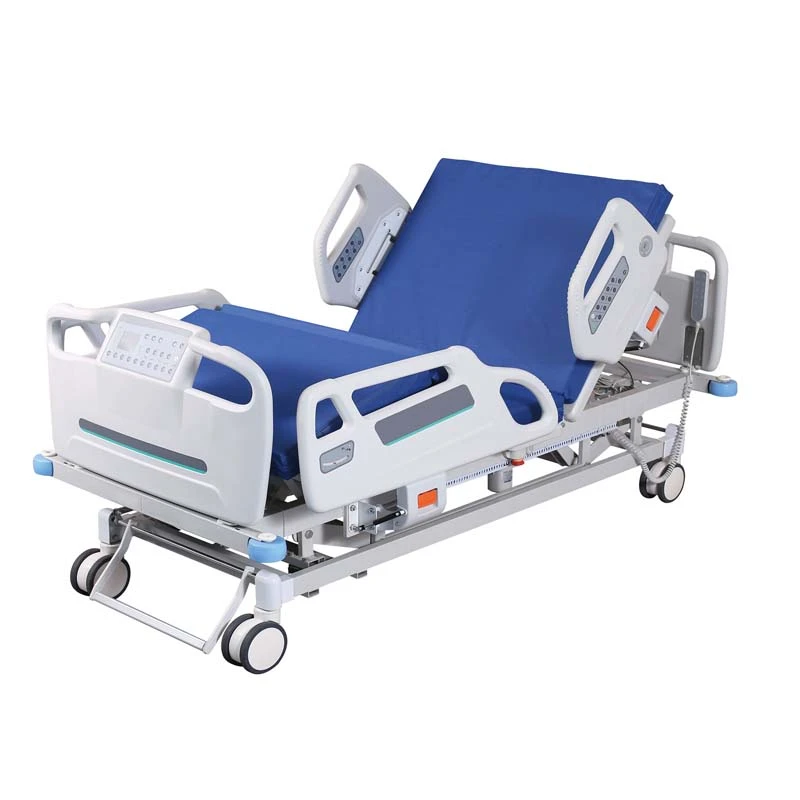
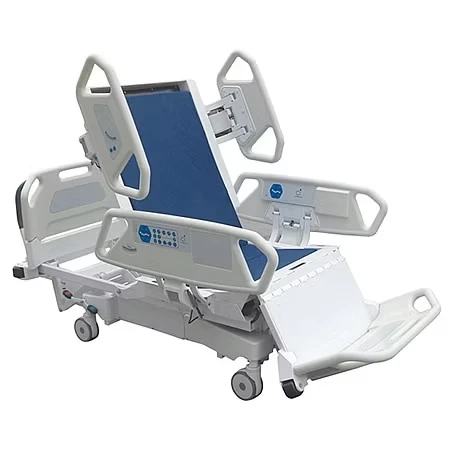
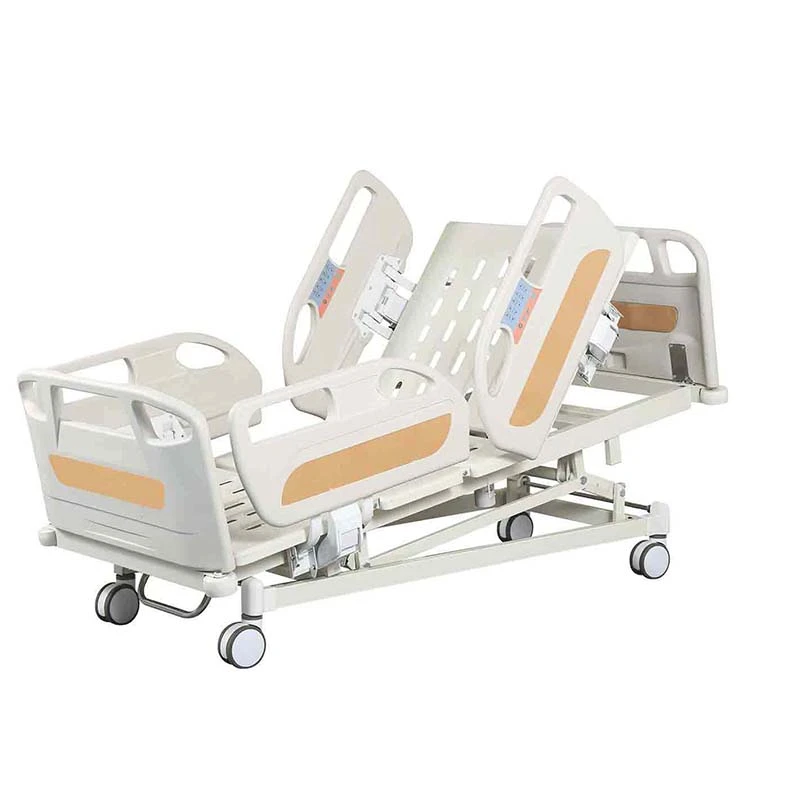
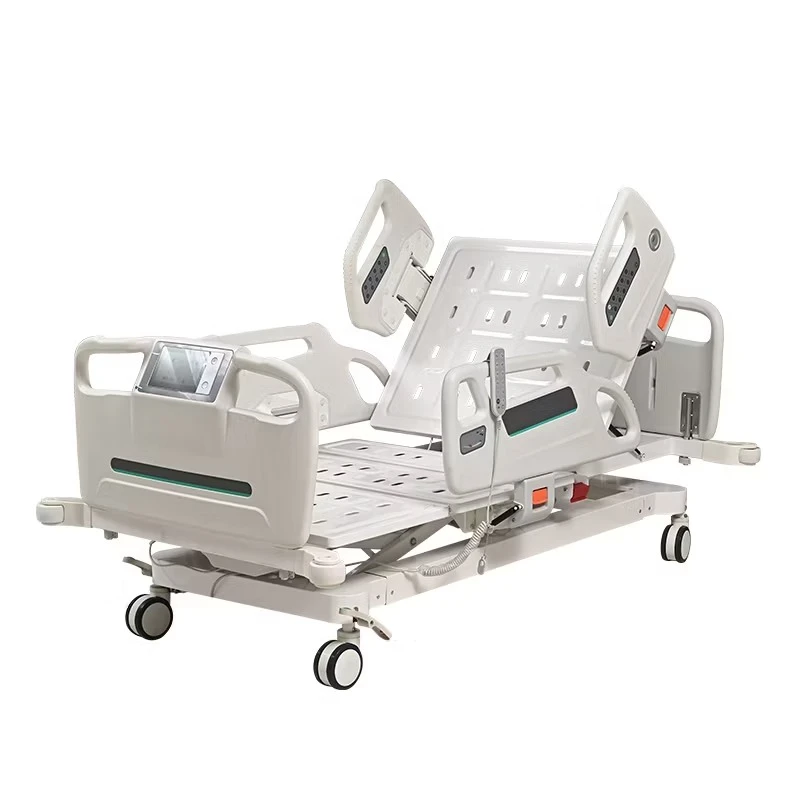
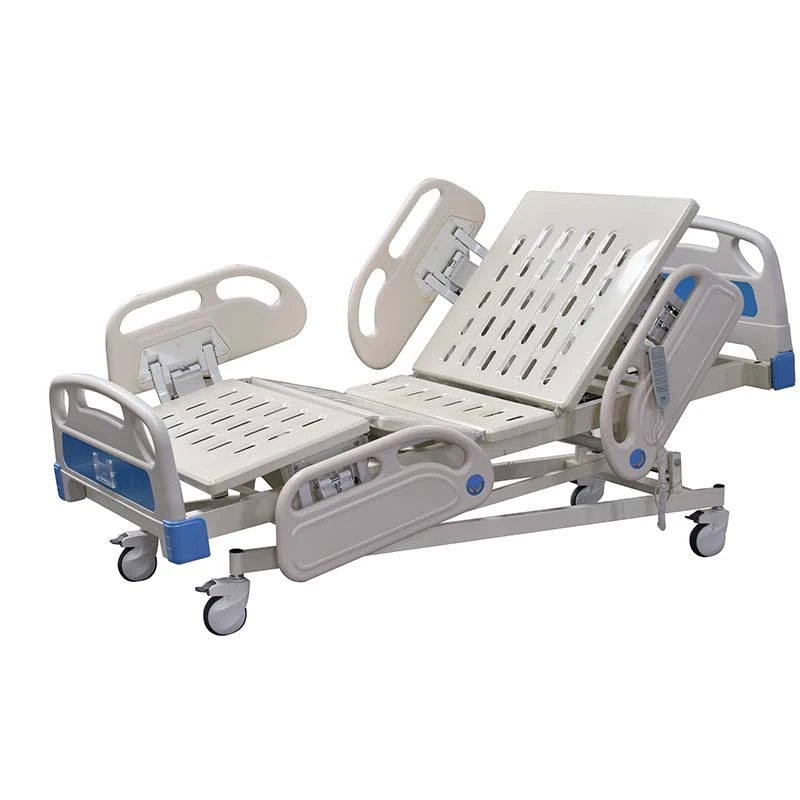
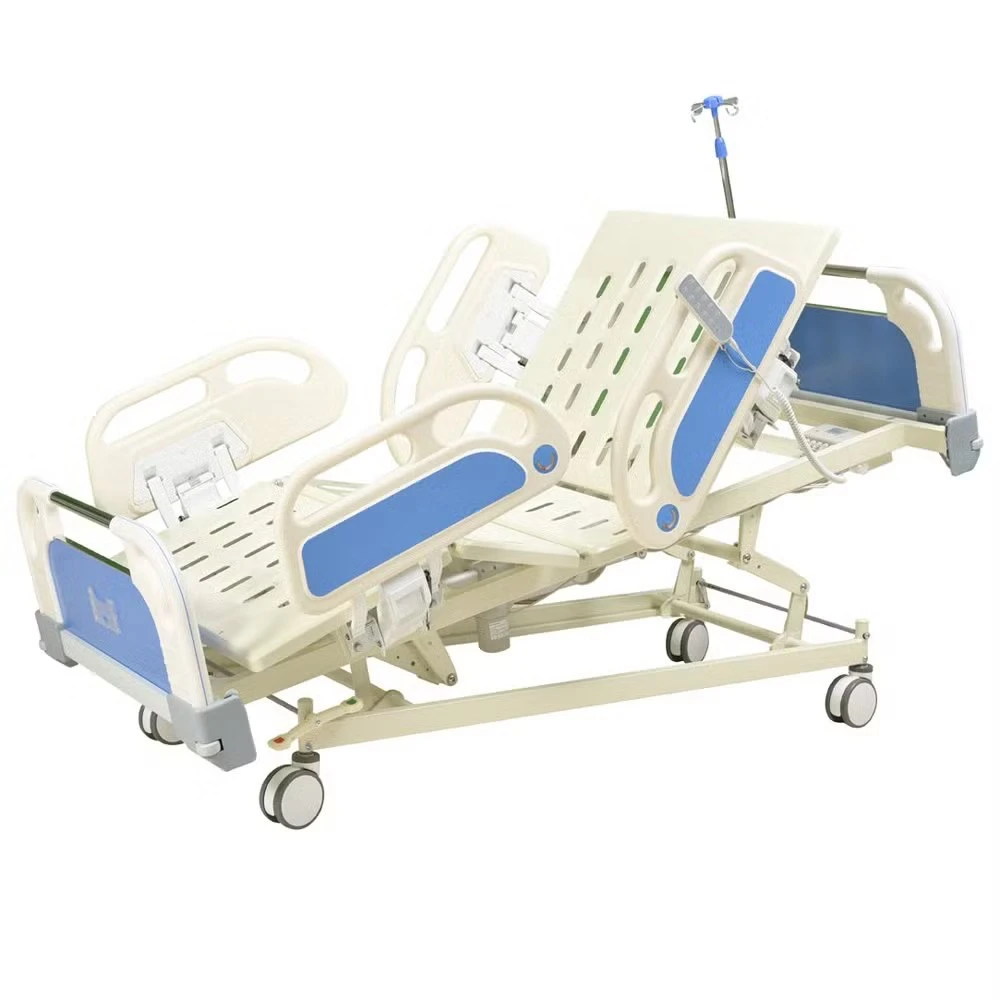
The Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is a specialized hospital area dedicated to providing critical care for patients with severe or life-threatening illnesses or injuries. A key component in delivering high-quality care in ICUs is the use of appropriate ICU bed types tailored to meet diverse patient needs. ICU beds are designed not only to provide comfort but also to facilitate medical procedures, enable monitoring, and improve clinical outcomes. There are primarily three main types of ICU beds: manual ICU beds, semi-electric ICU beds, and fully electric ICU beds.
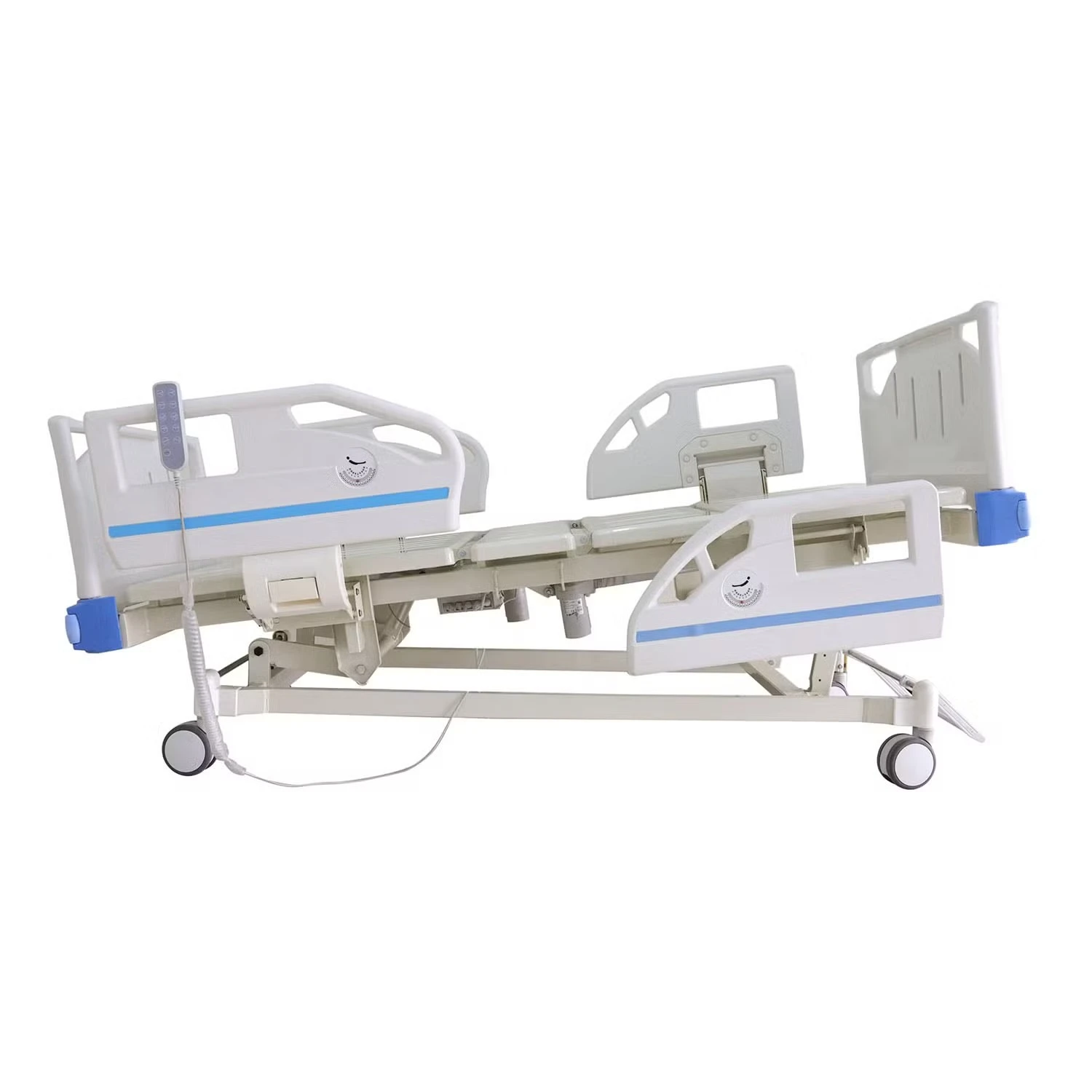
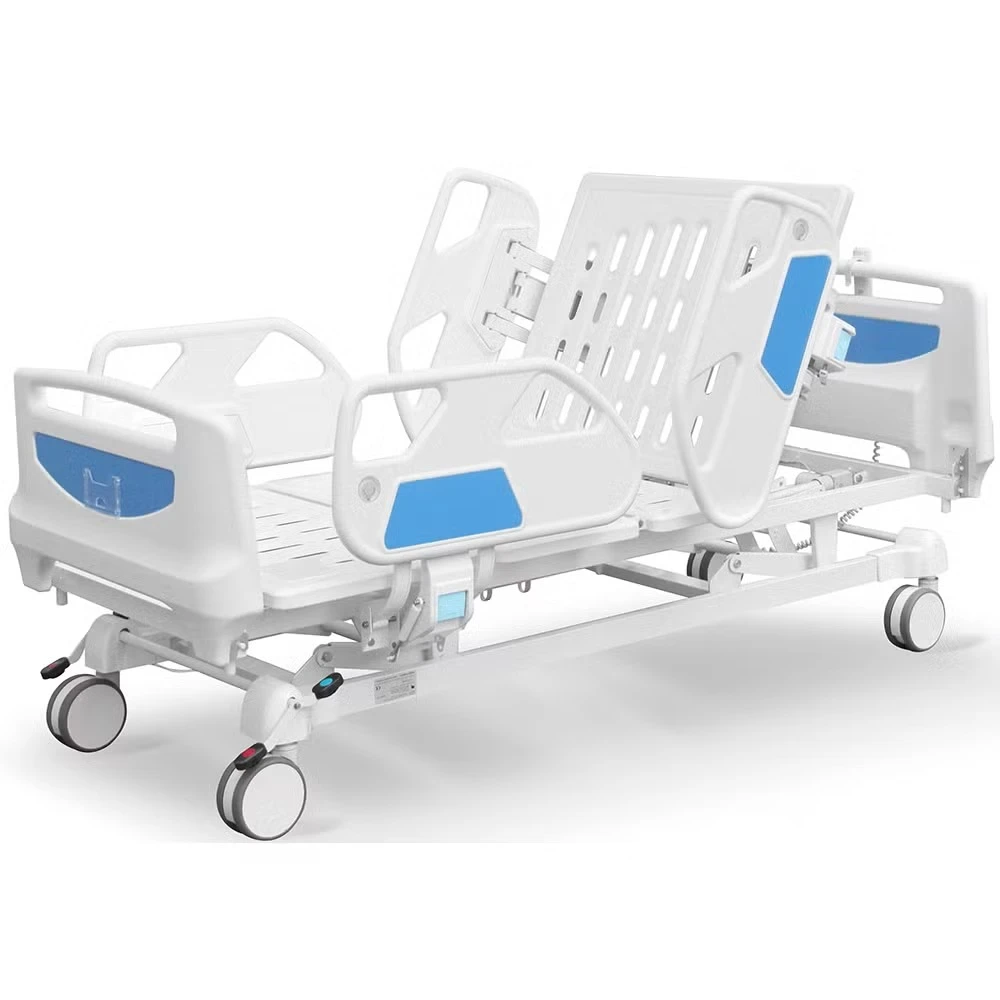
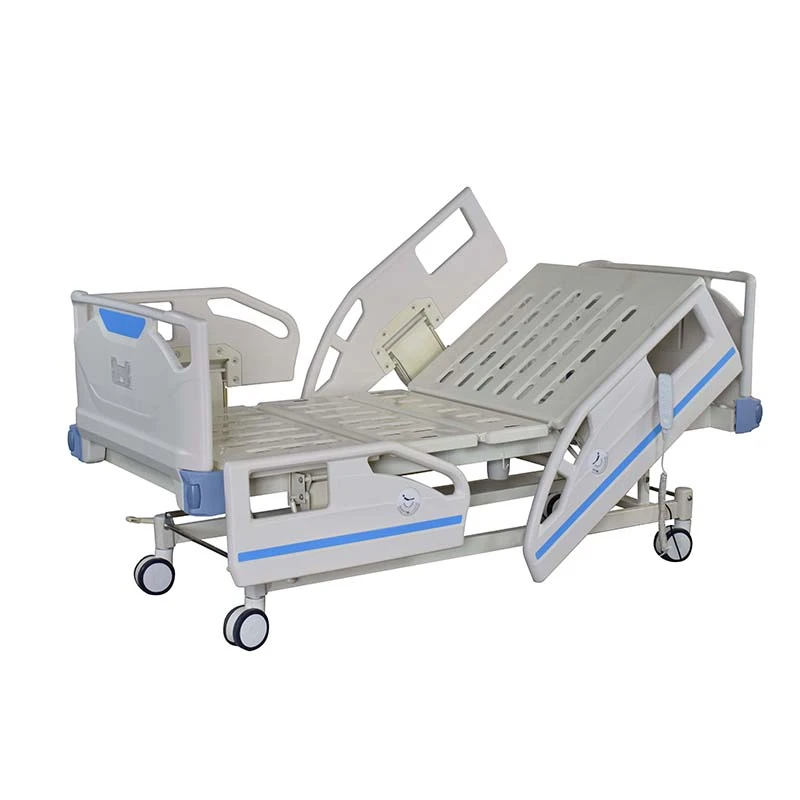
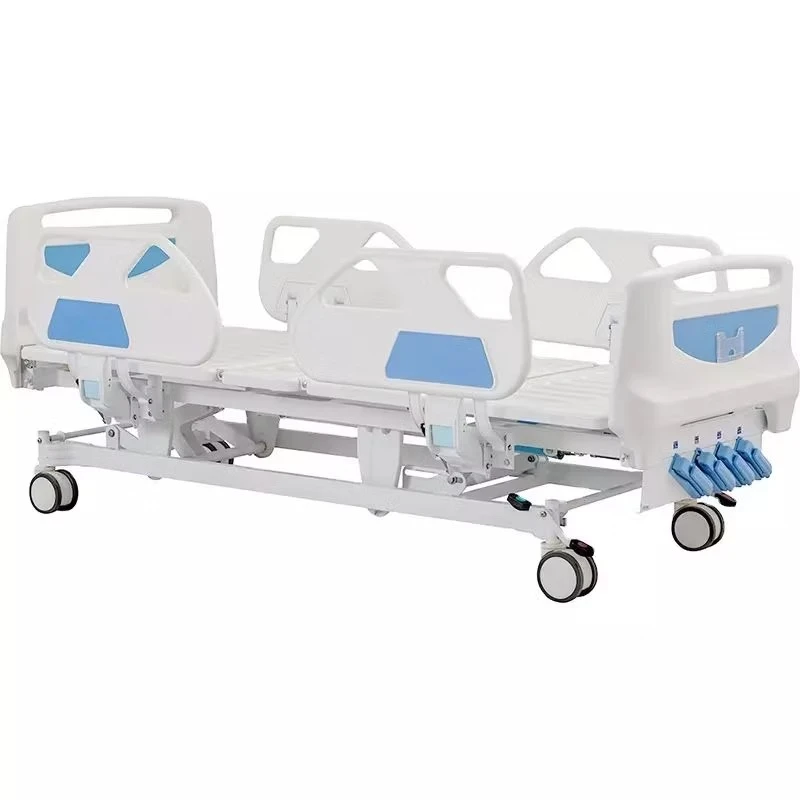
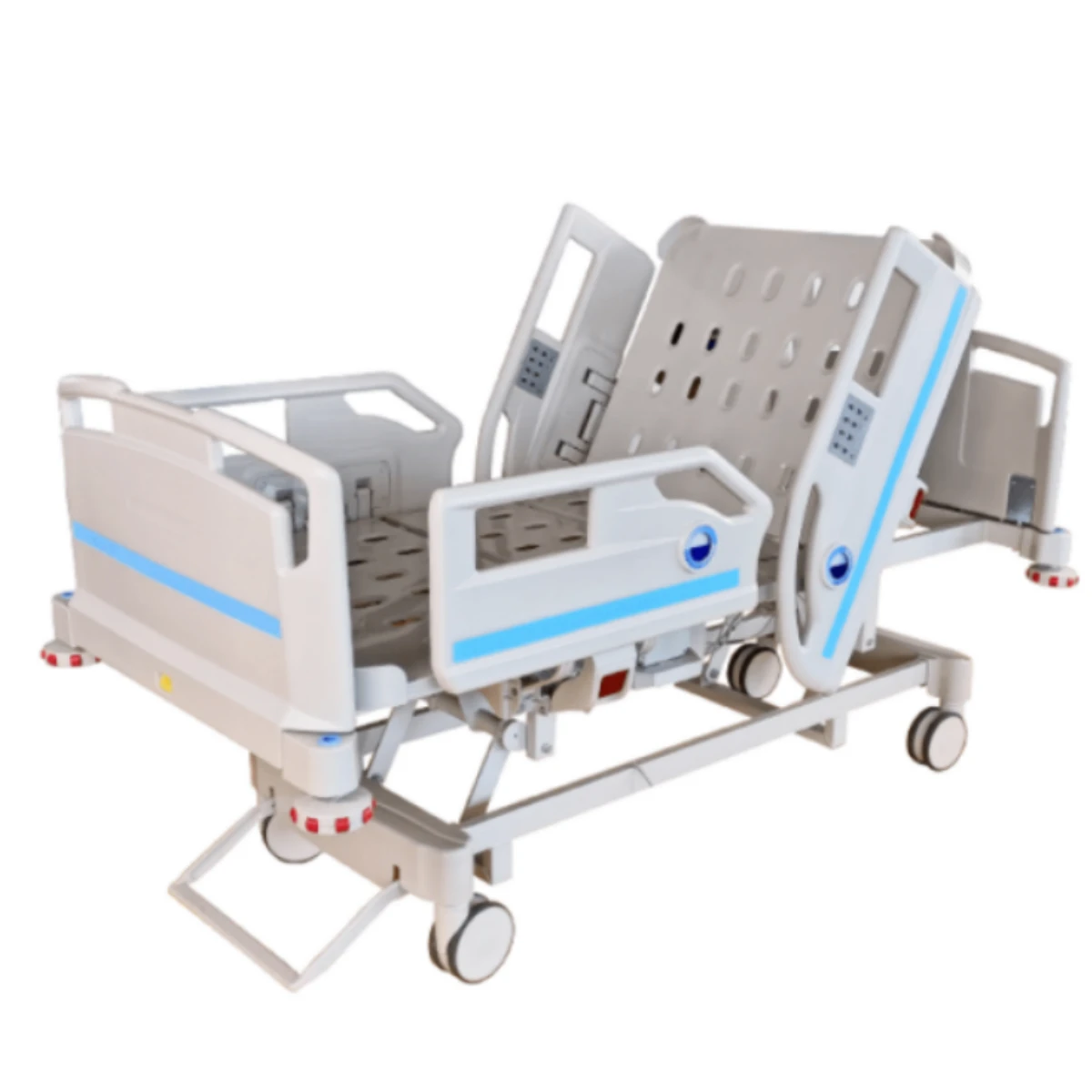
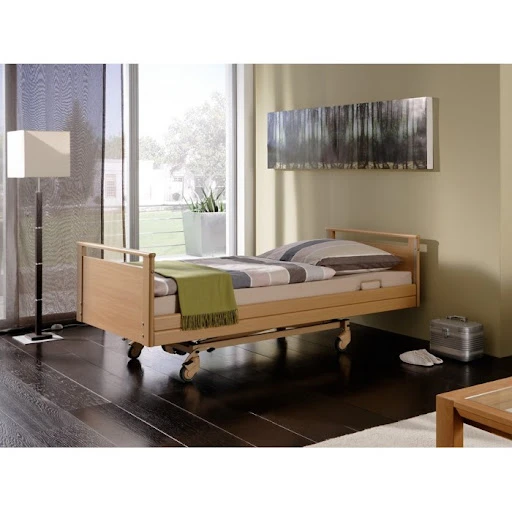
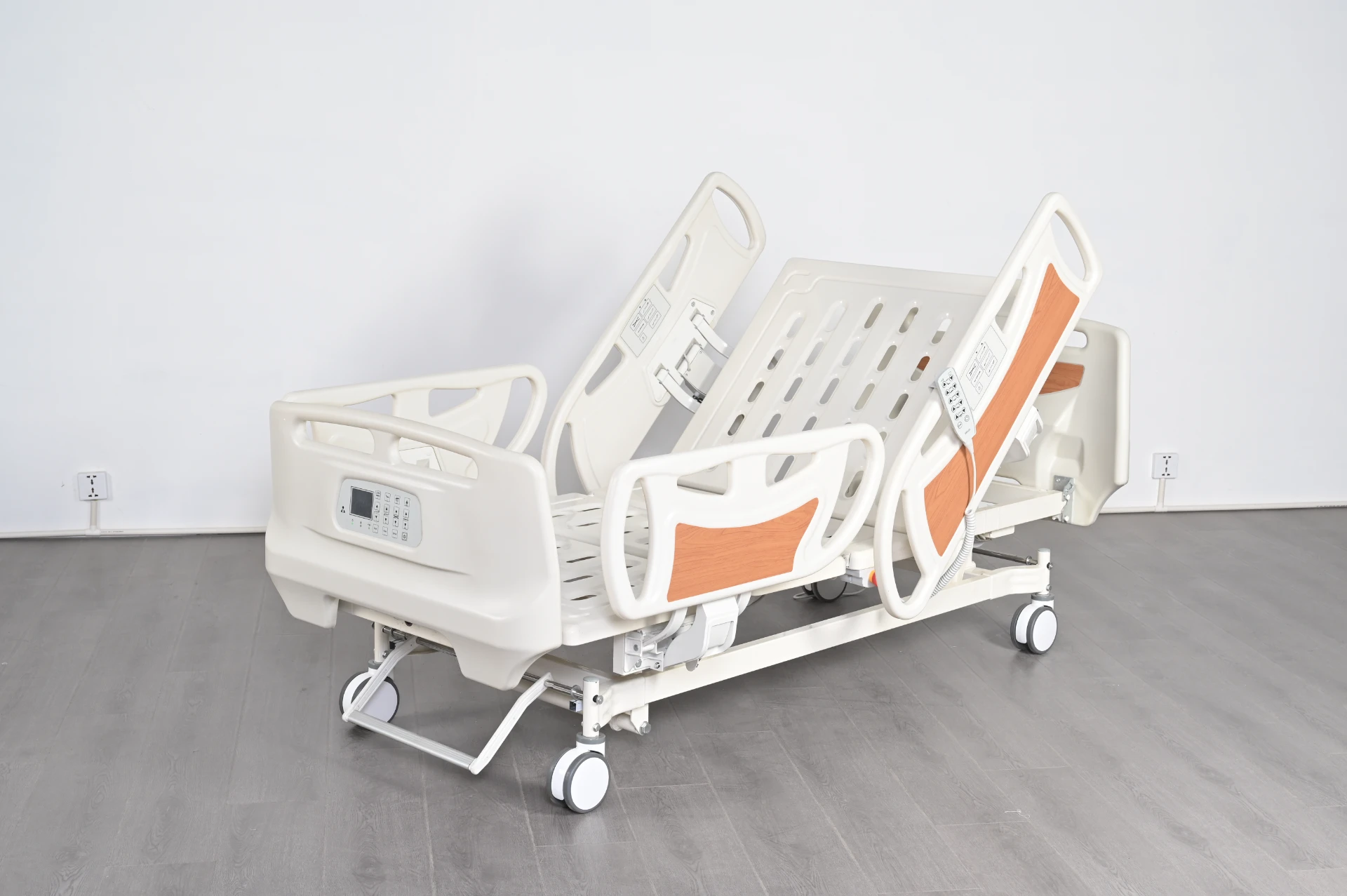
Manual ICU beds are operated via mechanical cranks to adjust the head, foot, and height positions. Although more cost-effective, they require more physical effort from healthcare providers and are less commonly used in modern ICUs. Semi-electric ICU beds incorporate motorized controls for positioning the head and foot sections, while height adjustments usually remain manual. These beds offer an intermediate level of convenience and functionality. Fully electric ICU beds provide motorized adjustments for all sections, including height, headrest, footrest, and advanced tilt functions such as the Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positions. These beds allow healthcare professionals to make precise, smooth adjustments with the push of a button, minimizing patient discomfort and optimizing medical care.
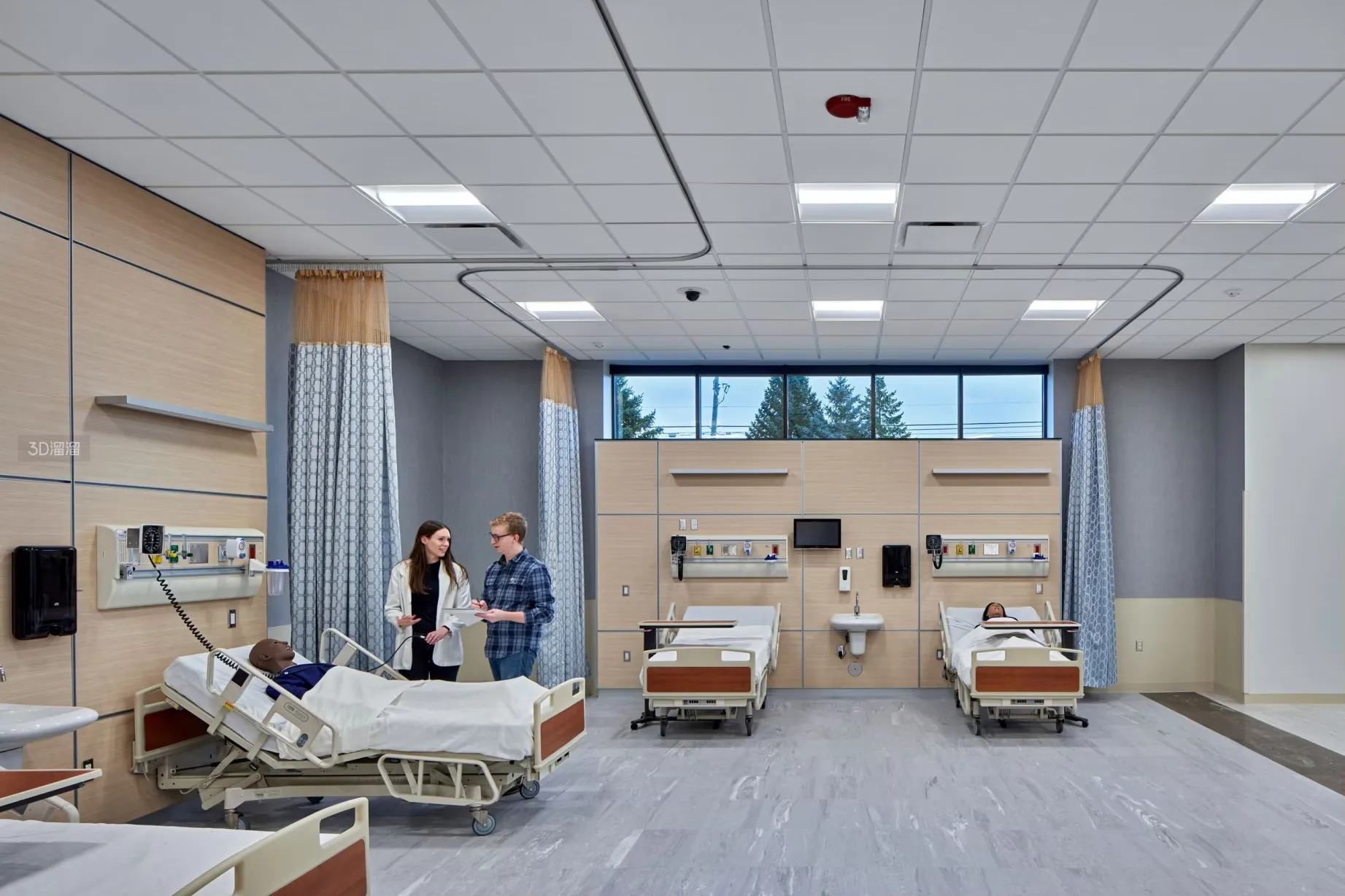
ICU Bed Patient Support and Design
Patient safety, comfort, and care accessibility are paramount in ICU bed design. The ICU bed patient experience is enhanced by features that support both patients and caregivers in an environment where timely and effective interventions are critical. Modern ICU beds are equipped with adjustable side rails to prevent falls, which is especially important for patients with limited mobility or altered consciousness. Many beds also include integrated weighing scales to monitor patient weight without the need for transfers, reducing the risk of injury.
Moreover, ICU beds are designed with durable frames to support patients of varying body types, including bariatric patients. Their surfaces are compatible with advanced pressure-relieving mattresses, which help prevent pressure ulcers, a common concern for immobilized patients. ICU beds also accommodate a wide range of medical devices such as ventilators, infusion pumps, and monitors, with built-in cable management systems that keep the environment organized and safe. The ergonomic design of ICU beds facilitates nursing care tasks like hygiene maintenance, wound care, and patient repositioning, reducing physical strain on staff while enhancing patient outcomes.
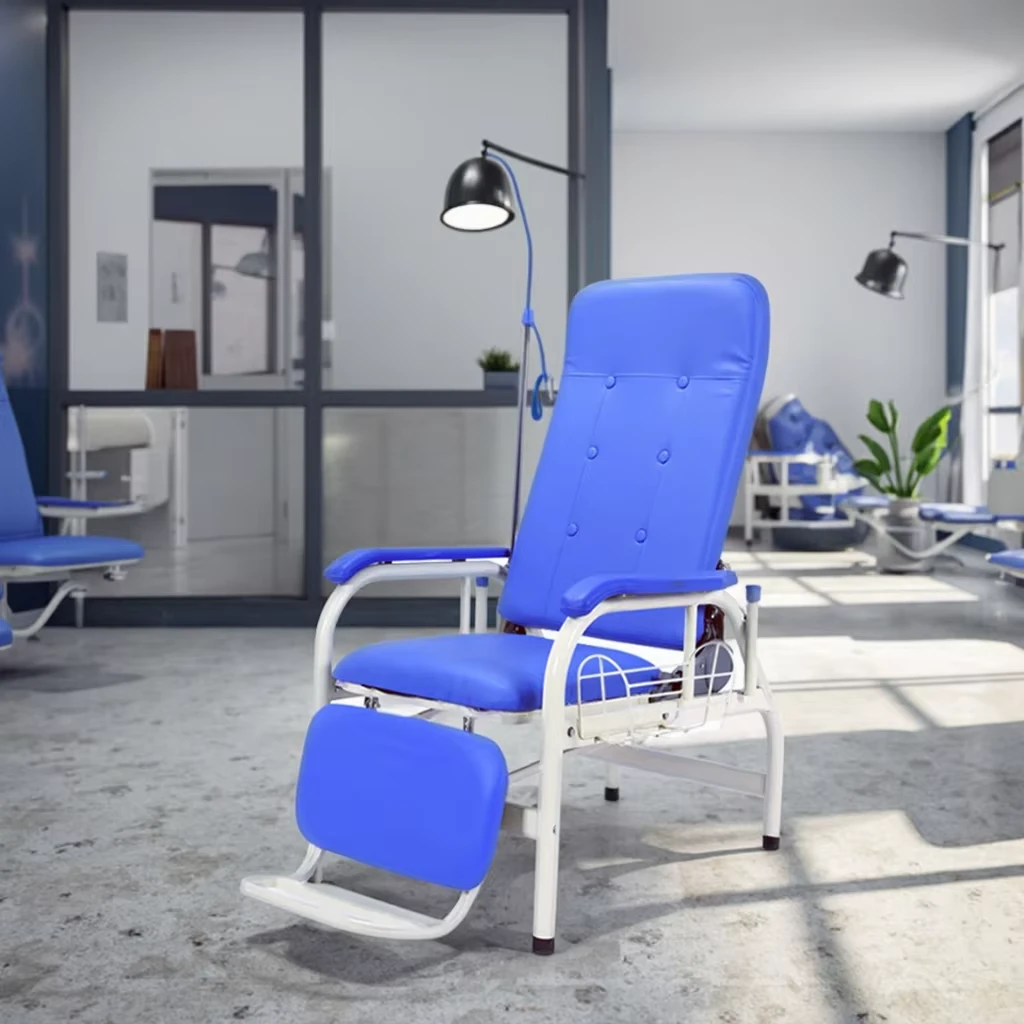
Hospital Bed ICU: Essential Attributes
When discussing hospital bed ICU models, several critical features distinguish these beds from standard hospital beds. One of the most important attributes is the availability of emergency CPR functions. These enable rapid flattening of the bed, crucial during cardiopulmonary resuscitation efforts. In addition, locking casters on ICU beds provide stability when stationary and ease of mobility when repositioning patients or moving beds between rooms.
Advanced ICU beds also support Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positions. The Trendelenburg position involves tilting the bed so that the patient’s head is lower than their feet, which can improve venous return to the heart and is used in certain emergency and surgical situations. Conversely, the reverse Trendelenburg position elevates the head above the feet, aiding respiratory function and reducing pressure on the lungs. Such positioning options are vital for optimizing hemodynamics and respiratory mechanics in critically ill patients.
Additional features often found in ICU beds include side rails with multiple locking positions, integrated nurse call buttons, and compatibility with various accessories such as overbed tables, IV poles, and bed exit alarms. Some models even incorporate built-in electronic interfaces for integration with hospital information systems, enabling better patient monitoring and record-keeping. These technological enhancements make hospital bed ICU models indispensable in modern critical care settings.
ICU Bed Types for Varied Clinical Needs
Different clinical scenarios require specific ICU bed types tailored to the patient population and medical condition. For example, pediatric ICU beds are designed with smaller dimensions and enhanced safety features such as higher side rails and child-friendly aesthetics to reduce anxiety. These beds also facilitate specialized care for neonates and infants.
Bariatric ICU beds are constructed with reinforced frames and wider platforms to safely accommodate obese patients. These beds support higher weight capacities and come with wider mattresses and side rails. Their robust design ensures stability and comfort while allowing caregivers to perform medical interventions effectively.
Neurological ICU beds provide special positioning options to manage patients with brain injuries or neurological conditions. These beds often include tilt and reclining features that help reduce intracranial pressure and support patient positioning for neurological assessments.
Neonatal ICU beds, often called incubators, offer controlled temperature and humidity environments for premature or critically ill newborns. These beds come equipped with specialized monitoring and access ports to facilitate neonatal intensive care.
Step-down ICU beds serve patients transitioning from intensive to general care. While less complex than full ICU beds, they still provide essential monitoring capabilities and positional adjustments needed for patient recovery.
ICU Beds FAQs
What are the different types of ICU beds available?
The main types of ICU beds include manual, semi-electric, and fully electric beds. Specialized models exist for pediatrics, bariatrics, neurological cases, and neonatal care.
How does an ICU bed support patient care?
ICU beds support patient care through advanced adjustability, safety features like side rails, integration with medical devices, and pressure ulcer prevention capabilities.
What features distinguish hospital bed ICU models?
ICU beds typically have electronic controls, emergency CPR functions, locking casters, Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positioning, and compatibility with various medical accessories.
Are there ICU beds designed specifically for children?
Yes, pediatric ICU beds have smaller dimensions, enhanced safety rails, and child-friendly designs to support young patients.
How do ICU bed types differ for specific medical conditions?
ICU beds vary by patient needs: bariatric beds support heavier patients with reinforced frames, neurological beds offer special tilt functions, and neonatal beds provide controlled environments for newborns.